When your crew member dons a spacesuit, they are preparing to enter one of the most extreme environments known to humankind—space. Whether for spacewalks, planetary exploration, or emergency situations, spacesuits are essential for survival beyond Earth’s atmosphere. Spacesuits do much more than just cover an astronaut’s body. They provide oxygen, temperature control, radiation protection, and …
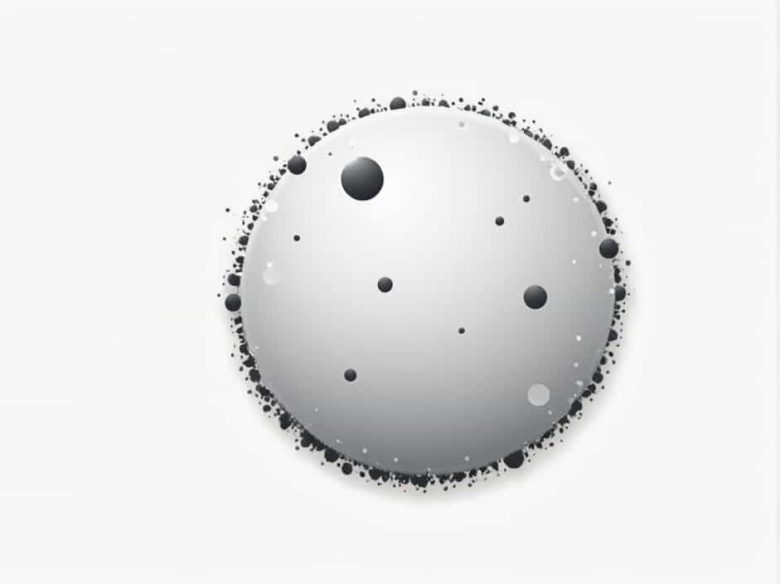
Globular clusters are among the most fascinating celestial objects in the universe. These dense, spherical collections of ancient stars orbit galaxies and provide valuable insights into the history of the cosmos. But where exactly do you find globular clusters, and what makes them unique? This topic explores their locations, characteristics, and importance in understanding our …
Millisecond pulsars are among the most fascinating objects in the universe. These rapidly rotating neutron stars emit beams of electromagnetic radiation at incredibly precise intervals, making them valuable tools for astronomers. Their extreme speeds, unique formation process, and role in astrophysics set them apart from regular pulsars. But what exactly are millisecond pulsars? What makes …
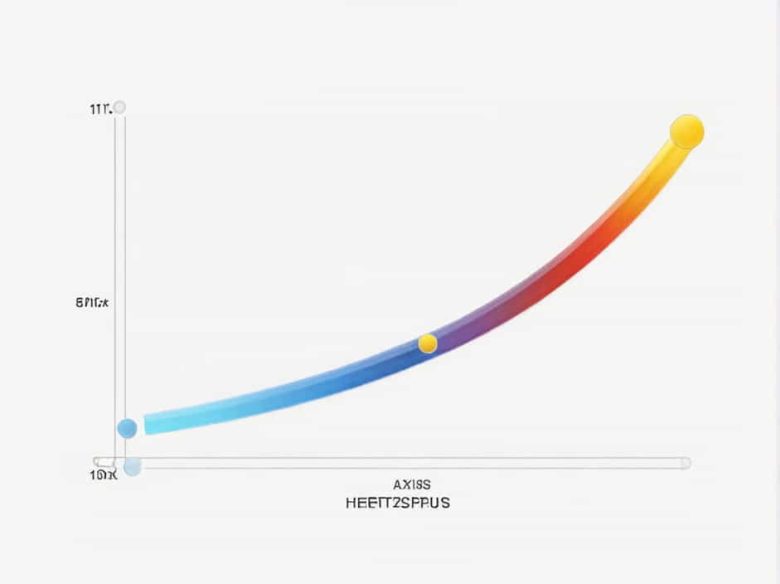
The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram is one of the most important tools in astrophysics. It visually represents the relationship between a star’s luminosity, temperature, and evolutionary stage. The diagram’s Y-axis plays a crucial role, as it represents a star’s brightness in various forms. But what exactly is plotted on this axis, and why is it significant? …
The X-Cel LX 5mm eyepiece 1.25-inch is a premium choice for amateur and professional astronomers looking to enhance their viewing experience. This eyepiece provides high magnification, sharp image quality, and comfortable eye relief, making it ideal for planetary and lunar observations. Whether you are stargazing in your backyard or using a telescope for deep-sky exploration, …
Many people assume that the Earth is a perfect sphere, but in reality, it is an ellipsoid. This means that while it is mostly round, it is slightly flattened at the poles and bulges at the equator. But why does the Earth take this shape instead of being a perfect sphere? The answer lies in …
When you look up at the night sky, you might notice a beautiful glow in some regions—these are nebulae. Often referred to as “star nurseries,” nebulae play a crucial role in the birth of stars. But what exactly makes these cosmic clouds deserving of this title? In this topic, we’ll explore why nebulae are called …
For centuries, humans believed that Earth was the center of the universe. This idea, known as the geocentric model, was widely accepted by ancient civilizations and supported by powerful institutions. However, one revolutionary thinker changed our understanding of the cosmos forever—the heliocentric model was born. In this topic, we will explore who created the heliocentric …
Stars come in various sizes, temperatures, and brightness levels. Among them, white stars are typically known for their high temperatures and luminosity. However, not all white stars shine brightly. Some are incredibly dim due to their small size, distance, or stage in stellar evolution. In this topic, we explore the dimmest known white star, analyzing …
White dwarfs are the final stage in the life cycle of medium-sized stars, including our Sun. These stellar remnants no longer produce energy through nuclear fusion and instead glow faintly as they slowly cool over billions of years. Among the thousands of white dwarfs identified by astronomers, some are exceptionally dim—so faint that they challenge …